This page is all about ripping media to populate a Plex library hosted on a Synology NAS server.
Drivers and Building Blocks
Demise of Video Station
For those of you who don’t know, Synology’s Video Station package provides a graphical front end to any video content you store on a Synology NAS. This post primarily came about because Synology, with its latest update to DSM (DiskStation Manager v7.2.2 onwards), dropped support of their own Video Station package.
NAS Upgrade
The second driver for this post was that my previous Synology NAS, a DS213+, was limited to upgrading only as far as DSM v6.2.4. This is due to Synology announcing EoL for this version of DSM being October 1, 2024. This forced me to upgrade my NAS Q2 2024 to a DS423+. Thus, with an increase from 2 to 4 bays, and the purchase of larger capacity drives (the MTTF of the existing decades old drives in the DS213+ was foreseeable!), I now had a great deal more storage available. Certainly enough to store several hundred movies and TV shows.
‘Plexed
So what to do if, like me, you used Video Station but wanted to ensure you can continue to be up-to-date with DSM – you might as well because it is inevitable that Synology will drop support for v7.2.1 at some point in the future.
There are a number of packages out there that can be installed on DSM which will give you equivalent functionality to Video Station. I decided to opt for Plex. In part, because it is readily available as an app on all the LG televisions we have at home, and also on our Android devices.
Best practice configuration of your video library under Plex is discussed later, but for the time being lets continue with rounding up all the other constituent parts…
Up to the Job
The other major piece of the “lets rip my whole video collection” challenge was the building of a high spec gaming PC in H1 2024. Once the DVD/Blu-ray disc has been decrypted to a file, the new PC reduced the whole ripping process from some 8+ hours per DVD disc, on an aging Sony laptop, to no more than 10 minutes! Which is just insane and a testament to the march of technology.
Let’s Get Ripping
With the aforementioned jigsaw pieces in place, I now had the major building blocks to create the “big picture”, namely ripping my entire video collection and have it available to play, on any device, anywhere.
To do so, three more pieces were required:
- A Blu-ray player
- MakeMKV
- Handbrake
Blu-ray Player
A list of Blu-ray players that are ideally suited to the task of ripping, and which can also be leveraged to rip 4K UHD discs, is listed in the MakeMKV forums.
Pioneer seem to be the most highly regarded brand. Alas, I have a decades old Samsung Blu-ray with a micro USB v1 connector. I’m sure a newer drive would be quicker, but I’m not sure I can justify the cost of a new one given that I don’t believe it would be night & day quicker. In addition, since I only have a collection of HD Blu-rays, there is no 4K requirement to force me to upgrade.
Obviously, things will change if I decide to go down the 4K UHD route which, given my ownership of OLED UHD televisions is likely but, for the time being, I’ll stick with what I’ve got. Regardless of whether it is a DVD, standard Blu-Ray or 4K disc being ripped, the principles outlined below remain pretty much the same.
MakeMKV
MakeMKV reads the contents of DVD/Blu-ray discs, decrypts them, and then writes the various titles (film + special features) out to your PC’s hard drive.
Download MakeMKV @ https://www.makemkv.com/download/
MakeMKV Registration key @ https://forum.makemkv.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=1053
MakeMKV is a fairly easy tool to use, but a great deal of tedious grunt work can be removed from the ripping process by editing your preferences to ensure that only English tracks (audio and subtitles) are selected.
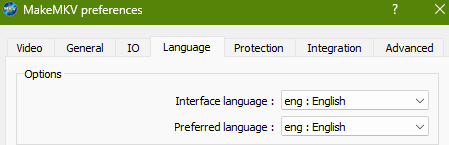
If you don’t do so, you will have to laboriously deselect the French, German, Japanese, Dutch, Portuguese etc tracks either in MakeMKV or later in Handbrake. Human error in this manual process will inevitably creep in and the processing of this extra data just gobbles up more CPU cycles, storage and, when streamed, your available bandwidth. You know it makes sense…
Video Title Selection
Ordinarily, it should be fairly self evident which title represents the main feature – in terms of gigabytes it will be the largest, with the greatest number of chapters etc. However, on some discs there can be one or more duplicates.
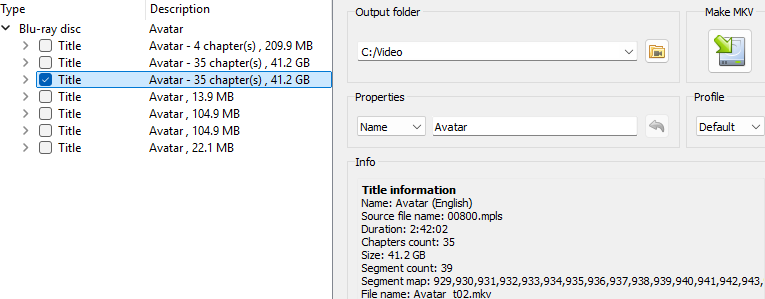
When you look more closely though, you will observe that each “duplicate” title references a different playlist (00800.mpls, 00801.mpls etc listed by MakeMKV as a Source file name), and each of these different playlists, although mostly identical, in terms of the segments they reference (listed by MakeMKV as a Segment map), will contain subtle differences.
As a general rule of thumb, opt to rip the lowest/even numbered track i.e. 0000.mpls or 0100.mpls, 0800.mpls etc. By way of example, Avatar has two “duplicated” tracks, but one of them uses playlist 00800.mpls which has the subtitles for the Na’Vi language burned in; that way when the Na’Vi are speaking to each other in their native tongue, you can automatically see/read the subtitled translation. If, on the other hand, you opted to rip the track with the 00801.mpls playlist, in the same Na’Vi scenes, you would have to pause the film and select the English subtitle track to understand what was being said. Unless of course you’re a native speaker of Na’Vi …
Audio Track Selection
It is worth playing back the ripped movie and looking at what audio tracks are available. Typically you may find a selection of:
- surround sound tracks (Atmos 7.1, Dolby 5.1, DTS, AC3 etc)
- commentary tracks
- audio description tracks (for people who are deaf or hard of hearing)
- isolated movie soundtrack
These can add to the resulting file size, so depending on your needs/wants you may wish to deselect these in MakeMKV prior to ripping the disc. If you forget at this stage, you can always remove them using Handbrake…
Handbrake
Handbrake is a tool that digests the decrypted & ripped DVD/Blu-ray MKV file created as output by MakeMKV (above), and converts it into whatever type of file your heart desires. Since the output from MakeMKV is raw and uncompressed data, Handbrake will use some form of compression algorithm to greatly reduce the size of the resulting file.
In my case, I wish to retain the visual and audio integrity of the media as best I can; otherwise I might as well use an online streaming service to watch them. The following Handbrake related sections outline how I achieve this.
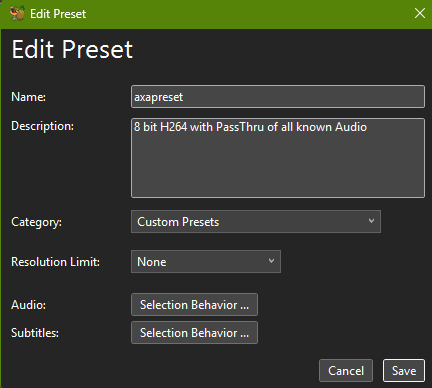
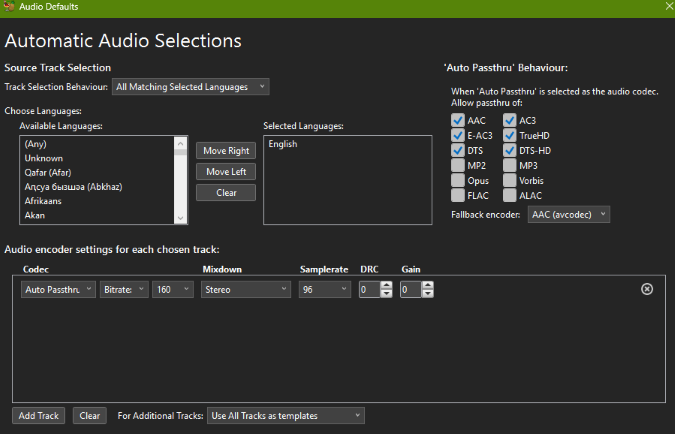
Audio Selection Behaviour
When creating my own pre-set, for the audio Selection Behaviour, use of Passthru retains the high quality of soundtracks; with anything else being encoded in AAC stereo.
Subtitles
Note that the Selection Behaviour for Subtitles is configured to only select English, but since we weeded out only the English versions when ripping the disc with MakeMKV, you may think specifying it again is somewhat superfluous.
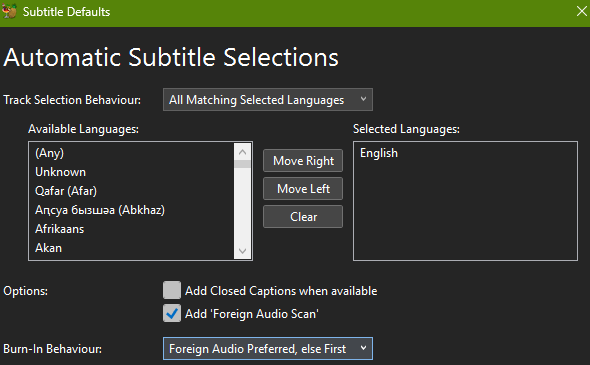
However, if a foreign language is spoken at some point in the film, HandBrake can perform a scan of the source title to try and detect if portions of the title are in a foreign language. If HandBrake does detects this, it will force the appropriate (English) subtitle track to be seen automatically. I’ve discovered that with problem titles (Avatar), that specifying the Burn-In Behaviour of Foreign Audio Preferred, else First did the trick of ensuring the desired outcome.
Video Encoding
Finally, the Video Encoder used is the H264 format. The newer H265 standard would result in a reduced file size, but it’s not as widely supported, hence the use of H264 for the time being.
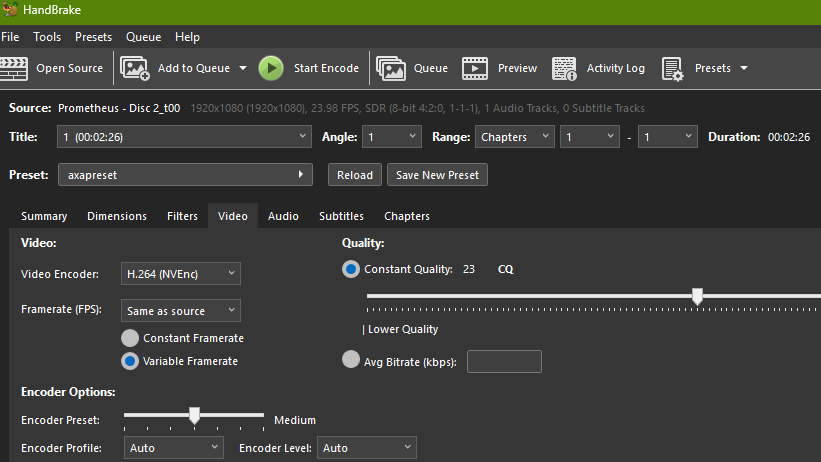
The Quality slider is set at a value recommended for 1080p Blu-ray. Since this is a logarithmic scale, the higher the quality setting, the significantly bigger the file. The consensus is that, from this value (23) onwards, it’s a case of diminishing returns. Obviously, this would require tweaking for lower quality DVDs and higher quality UHD discs.
Lastly, since my PC has an NVidia graphics card, I configure the Video Preferences to use the associated driver to encode the files. Doing this greatly reduces the time taken to encode the files.
Once the discs are ripped and the resulting files are ready to be moved over to the NAS, the configuration of the media library has to be considered.
What About 3D Movies?
Having built a new PC, purchased a new NAS, and a sim racing rig, it’s safe to say that 2024 turned out to be a very expensive year! Striving for further sim racing immersion, I subsequently bought a Meta Quest 3 headset in Q4. Getting this VR headset to work alongside various different sim racing games was a headache. However, the Quest 3 has proved more than useful for other things. In terms of AV experience, use of the Skybox app has been an eye opener for movie watching, and the possibility of using it for 3D movies intriguing…
We are going off at a bit of a tangent here though. Granted you can store 3D movies under Plex control, however unless you own a 3D capable TV or projector, you can’t readily watch them from Plex. Furthermore, there is not a native Plex app for the Meta Quest; although I’ve yet to attempt to use the browser version of it via Meta Quest. Regardless, Skybox readily reads video files from a NAS, and the PLex naming conventions make location of any content an easy task.
Procedure for 3D Rips
The procedure for ripping a 3D Blu-ray is pretty much the same as before, namely the use of MakeMKV to decrypt the disc and write the contents to a hard drive on your PC.
MakeMKV Caveat
There is one caveat to using MakeMKV, and that is to ensure that you select the tick box associated with “Mpeg4-MVC-3D”. If this is not selected, the utility which actually creates the 3D movie will not work, and that utility is…
About BD3D2MK3D
After using MakeMKV to rip the disc, we switch our attention away from Handbrake, and instead use BD3D2MK3D (Blu-ray Disc 3D to Matroska 3D). The utility can be downloaded from:
https://www.videohelp.com/software/BD3D2MK3D
At the time of writing, v1.33 is the current version of BD3D2MK3D but, in order to run, BD3D2MK3D has a further two other dependencies. These need to be sourced, downloaded and installed beforehand. These are:
- Java Runtime Environment
BD3D2MK3D requires a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) to execute. Oracle is the holder of everything Java related, however Oracle require payment to use their JRE. Far better and cheaper (free!) is to install the open source equivalent. This is where Eclipse Temurin comes to the fore. To download, go to https://adoptium.net/en-GB/temurin/releases/
At the time of writing, the current version was 21.0.5+11-LTS and if you’re a Win11 user, you’d be best advised to download the version for Windows x64 JRE MSI (filename:OpenJDK21U-jre_x64_windows_hotspot_21.0.5_11) Note all those keywords in bold, and also that the JDK is the Java Development Kit; this is a much larger install containing a load of superfluous stuff above & beyond the JRE. - AviSynth+
The installation media for AviSynth+ is located on GitHub. Here, you’ll have to scroll down to the Assets section to locate the appropriate media. At the time of writing v3.7.3_20230715 was the latest release for MS Windows (filename:AviSynthPlus_3.7.3_20230715.exe)
With a JRE and AviSynth+ installed, you can run BD3D2MK3D.
Using BD3D2MK3D
Keep in mind that the following pertains to creating a MKV video file which can be subsequently watched on a Meta Quest 3 VR headset. As such, other settings may have to be tweaked if the end game is different. Here’s what to do for each of the tabs presented:
- Open MKV 3D
When BD3D2MK3D executes, the first thing that needs to be done is to click on the Switch to 3D MKV button. This allows BD3D2MK3D to read the MakeMKV output (a MKV file) as input. - Select stream
I deselect all but the primary Audio track - Title & tags
Enter the title of the movie – this field is mandatory, all the other fields are optional. - Cover art
I don’t bother with this… - Options and Go!
Stereoscopy: deselect the Half tick box. Using the implied full stereoscopy gives a perceptibly sharper image. In addition movement across the screen is noticeably sharper and less jerky.X264 (h264 AVC) encoder options: change Level from do not force to force 5.0 (Full, 1080p)Go!: update the Project (temp) folder: field to the drive/directory of your choice.
In the examples below, I use my secondary SSD D:\Videos\3DMKV
Note that when you click on the go button, BD3D2MK3D will nag you to ensure that you are sure that you want to go ahead, and yes you jolly well do.
How long the next two steps take are really dependant upon your hardware.
Once you’ve pressed the Go button BD3D2MK3D will scurry away, create a folder and populate it with about 30 files taking up anywhere between 30-60Gb. So make sure you have enough space available on your target drive!
Once complete, a window will appear.
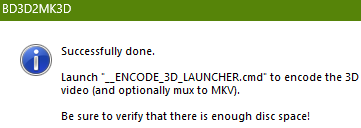
At this point fire up a Windows command prompt, and navigate to the Project (temp) folder: you specified previously. In my case, this is D:\Videos\3DMKV\Avatar\MKV3D and then enter the command __ENCODE_3D_LAUNCHER
At this point the window shown below will appear, and you should go and make a beverage of your choice and perhaps start reading a book because this can take, and again it’s dependant upon your hardware capability, a long time.
Once the BD3D2MK3D process has completed you will be able to move the resulting file over to the movie folder on the Synology NAS and watch the movie on a Meta Quest 3.
Plex Configuration
Due to the simplicity of installation of any package on DSM, there’s not a lot to say about Plex installation and configuration, but here are a handful:
- When initially opening Plex from DSM to configure it, the URL might be incorrect. Read this Synology Community forum post for details.
- To ensure the correct collection of online data by Plex, ensure that the file for the title is spelt correctly and includes the year of release in brackets i.e.
Alien (1979).mkv - If there are multiple editions of a title, retain the year of the original release for both editions, and ensure the title name is suffixed with edition metadata, as per the example below:
/Alien (1979)
Alien (1979) {edition-Theatrical Version}.mkv
Alien (1979) {edition-Director's Cut}.mkv
Additional Info - Follow the Plex recommended method of organising your video collection by using a directory structure. See the Alien example below. After that, ensure that “Special Features” tracks are renamed to some meaningful title and then copy them into the appropriate directory.
/Movies
/Alien (1979) {edition-Theatrical Version}
/Behind The Scenes
/Deleted Scenes
/Featurettes
/Interviews
/Other
/Scenes
/Shorts
/Trailers
Alien (1979) {edition-Theatrical Version}.mkv
/Alien (1979) {edition-Director's Cut}1
Alien (1979) {edition-Director's Cut}.mkvThis approach saves the hassle of having to rename a title and suffixing it with identifying metadata i.e.
Alien Deleted Scenes.mkv
to
Alien Deleted Scenes-deleted.mkv
A tedious task no matter how large or small your video collection! It’s a great deal easier to ensure a sensibly named file is moved into the appropriate directory.
Plex References
Plex Media Package for Synology
Naming and Organising Your Movie Files
Naming and Optimising You TV Shows Files
LAN Streaming
An initial issue I encountered was the streaming of high quality rips; typically Blu-rays with loss-less 7.1 HD soundtracks. It transpired that, as shipped, LAN streaming of such titles was constricted. To resolve this, go to Settings > Plex Web > Quality and, under Home Streaming, change the Video quality to Maximum. This prevents any throttling of such rips and ensures that Plex continues to Direct Stream them.
Manipulating MKV Files
https://mkvtoolnix.download/downloads.html
- Note that different editions of a title should be stored in their own uniquely identified directory ↩︎


